Satellite Antenna Gain Equation
These are all multiplied together to give the overall efficiency.
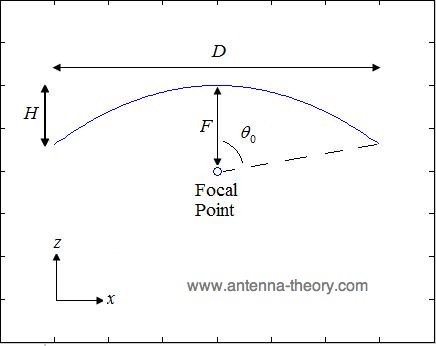
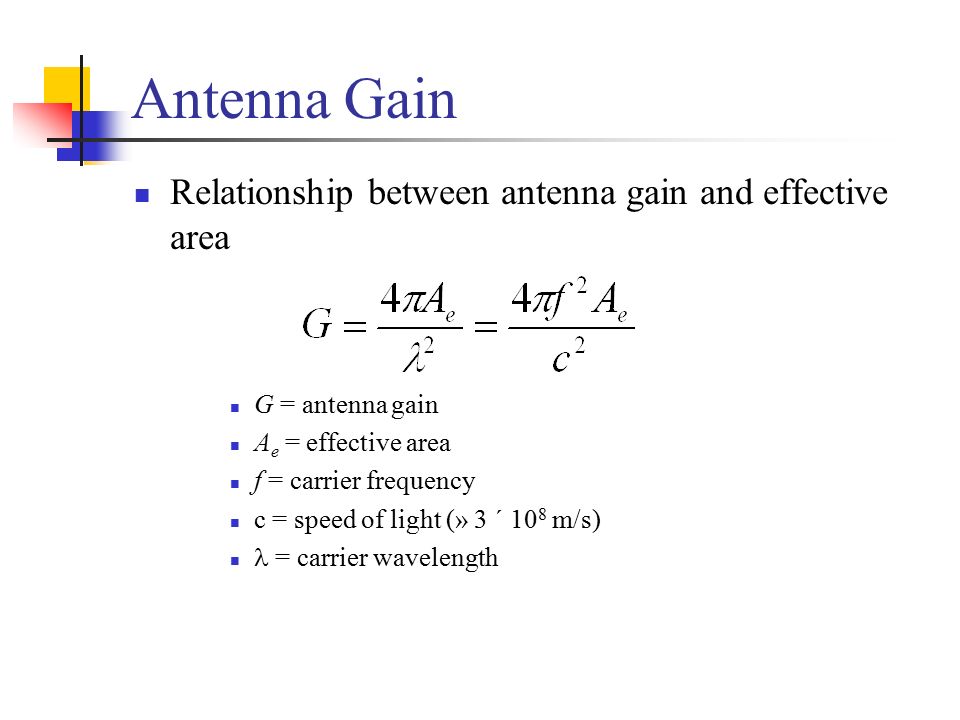
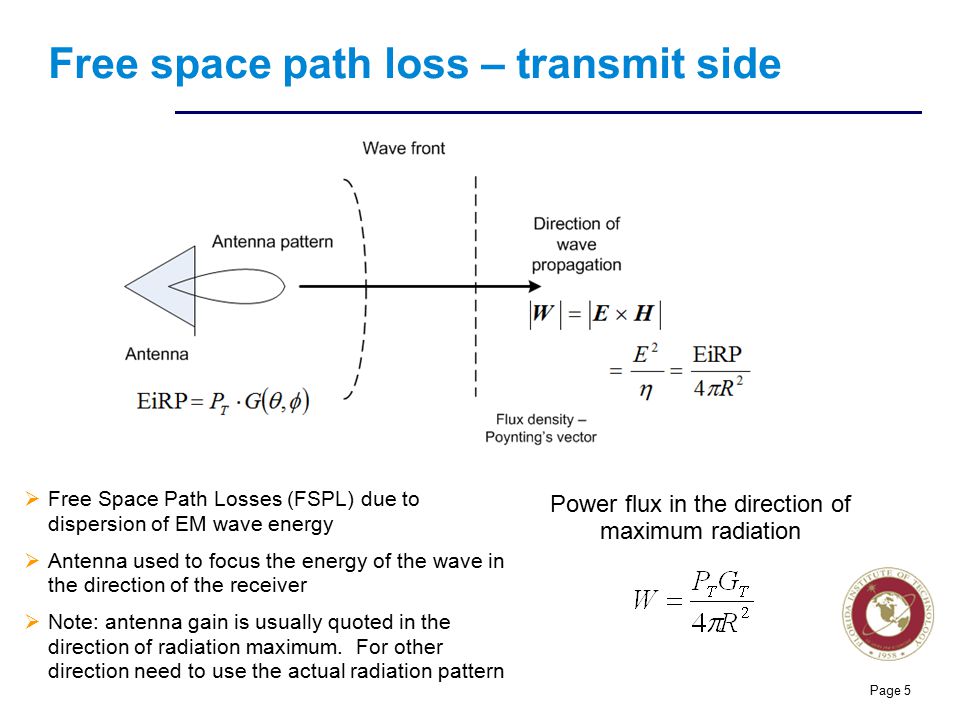
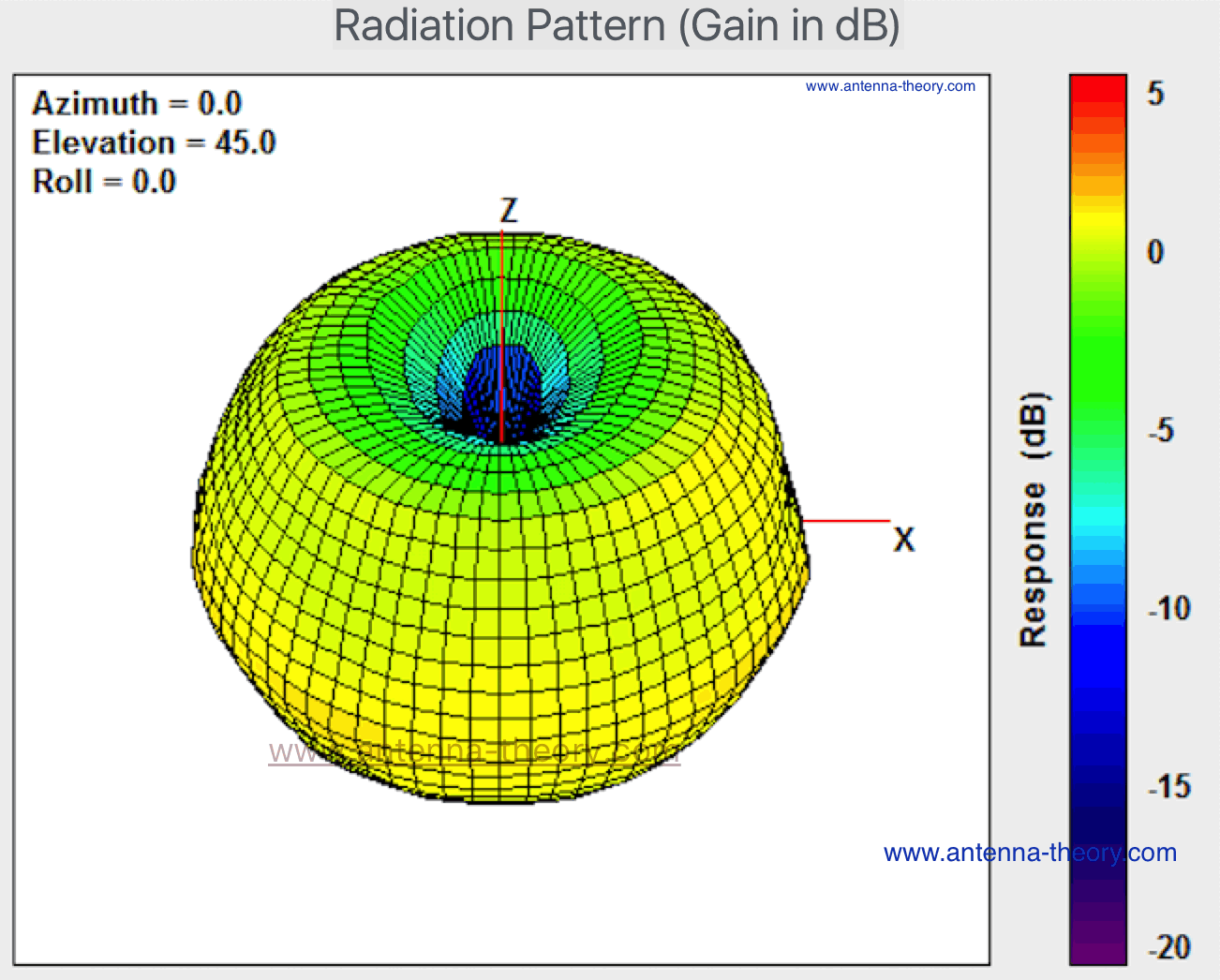
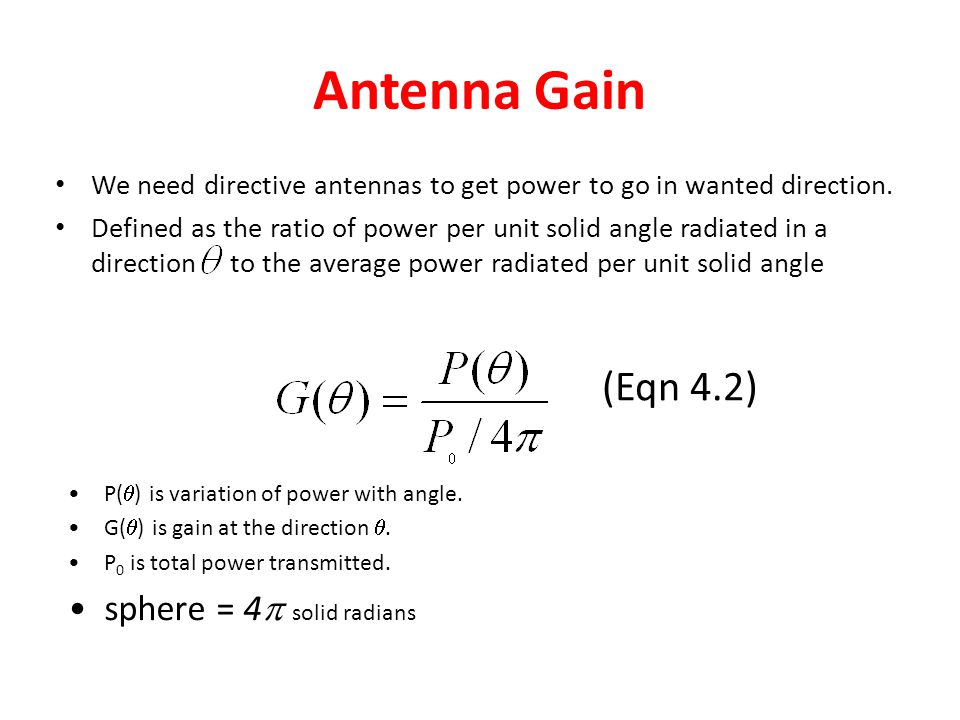
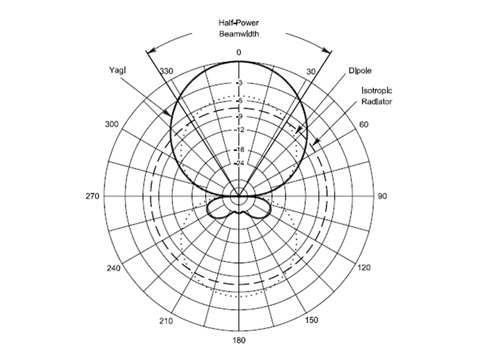
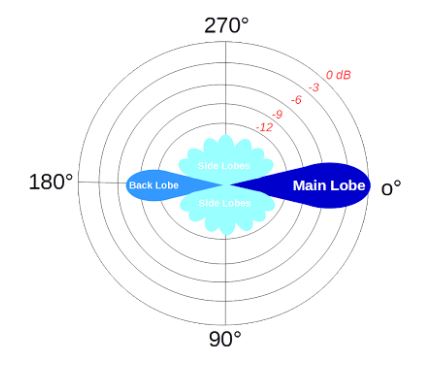
Satellite antenna gain equation. Antenna gain can only be achieved by making an antenna directional that is with better. Antenna factor or correction factor is defined as the ratio of the incident electromagnetic field to the output voltage from the antenna and the output connector. The receive antenna will have a gain that will also be calculated in accordance with equation 14 11. The gain increases with the square of the ratio of aperture width to wavelength so large parabolic antennas such as those used for spacecraft communication and radio telescopes can have extremely high gain.
In the overall gain formula for the antenna an efficiency factor is included. Antenna gain calculator example. Antenna gain calculator equation. The parabolic reflector antenna gain efficiency is dependent upon a variety of factors.
Directivity can be as low as 1 76 db for a real antenna example. If an lna is mounted at the back of the receive antenna feedhorn as is common enter its gain at this point. The gain of a real antenna can be as high as 40 50 db for very large dish antennas although this is rare. In their place is the descriptor of antenna capture area as one of two important parts of the transmission formula that characterizes the behavior of a free space radio circuit.
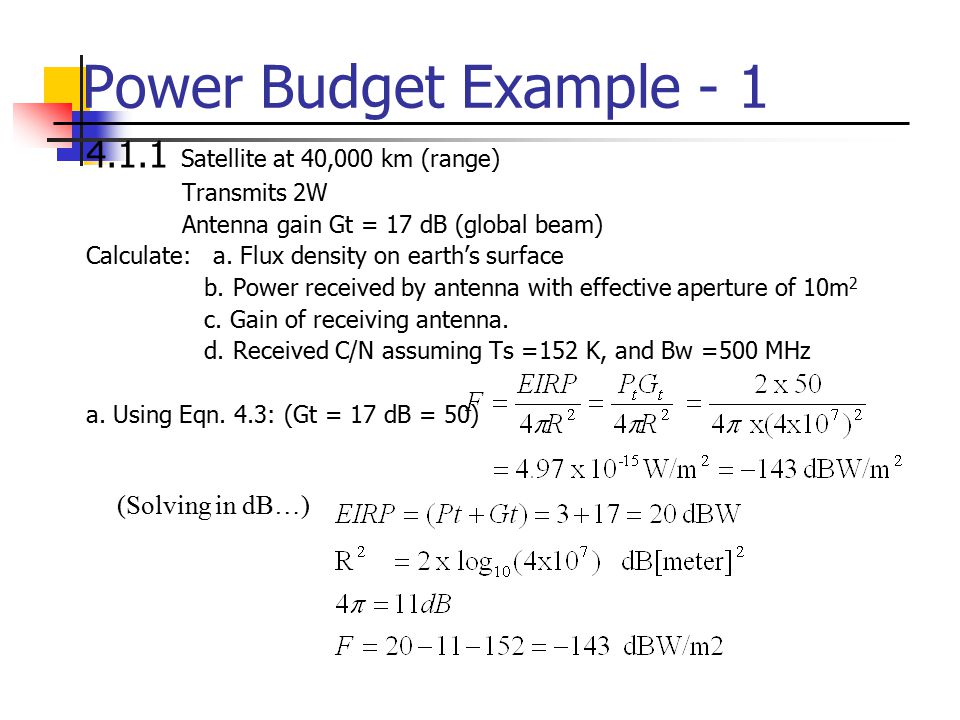
Antenna gain is the measure of amount of boost provided to the input sigal by the antenna. Antenna efficiency 0 7 antenna diameter 4 2 meter antenna frequency 6 ghz output gain dbi 47. Typically this may be between 50 and 70 dependent upon the actual antenna. Applying the above formula to the 25 meter diameter antennas often used in radio telescope arrays and satellite ground antennas at a.
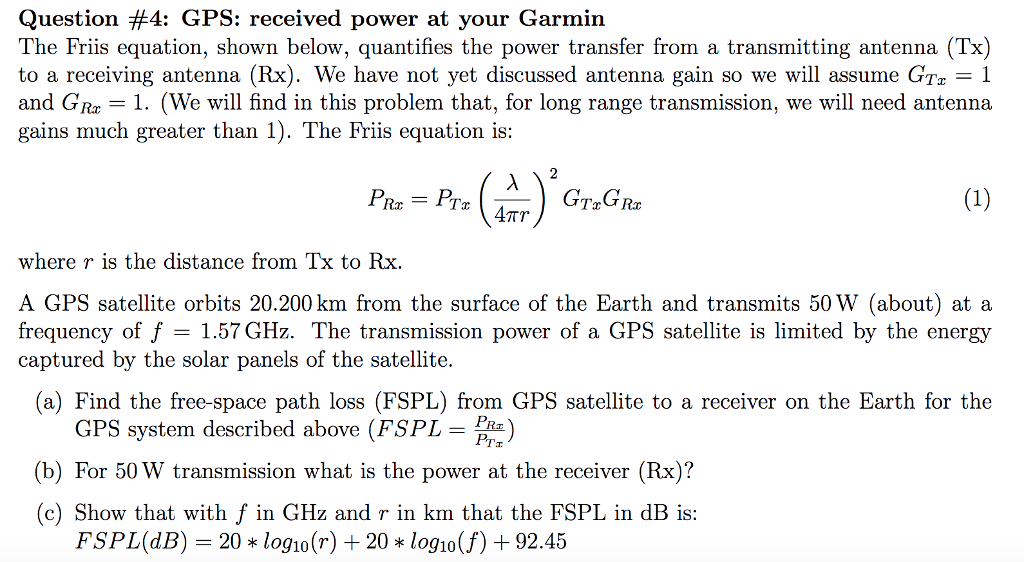
Friis original idea behind his transmission formula was to dispense with the usage of directivity or gain when describing antenna performance. On this page we introduce one of the most fundamental equations in antenna theory the friis transmission equation the friis transmission equation is used to calculate the power received from one antenna with gain g1 when transmitted from another antenna with gain g2 separated by a distance r and operating at frequency f or wavelength lambda.