Satellite Antenna Gain Formula
Antenna gain calculator equation.
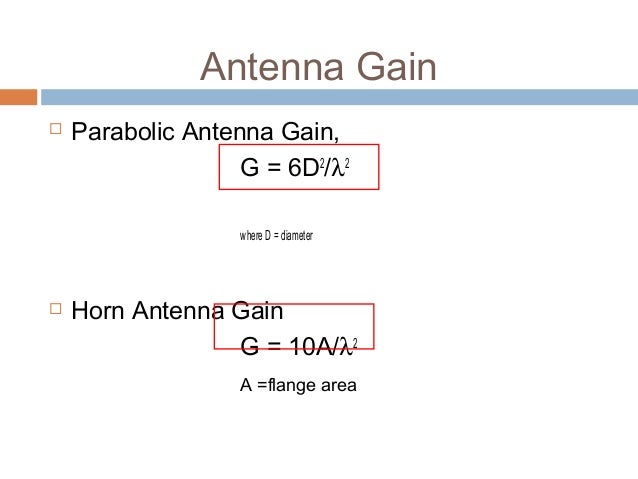
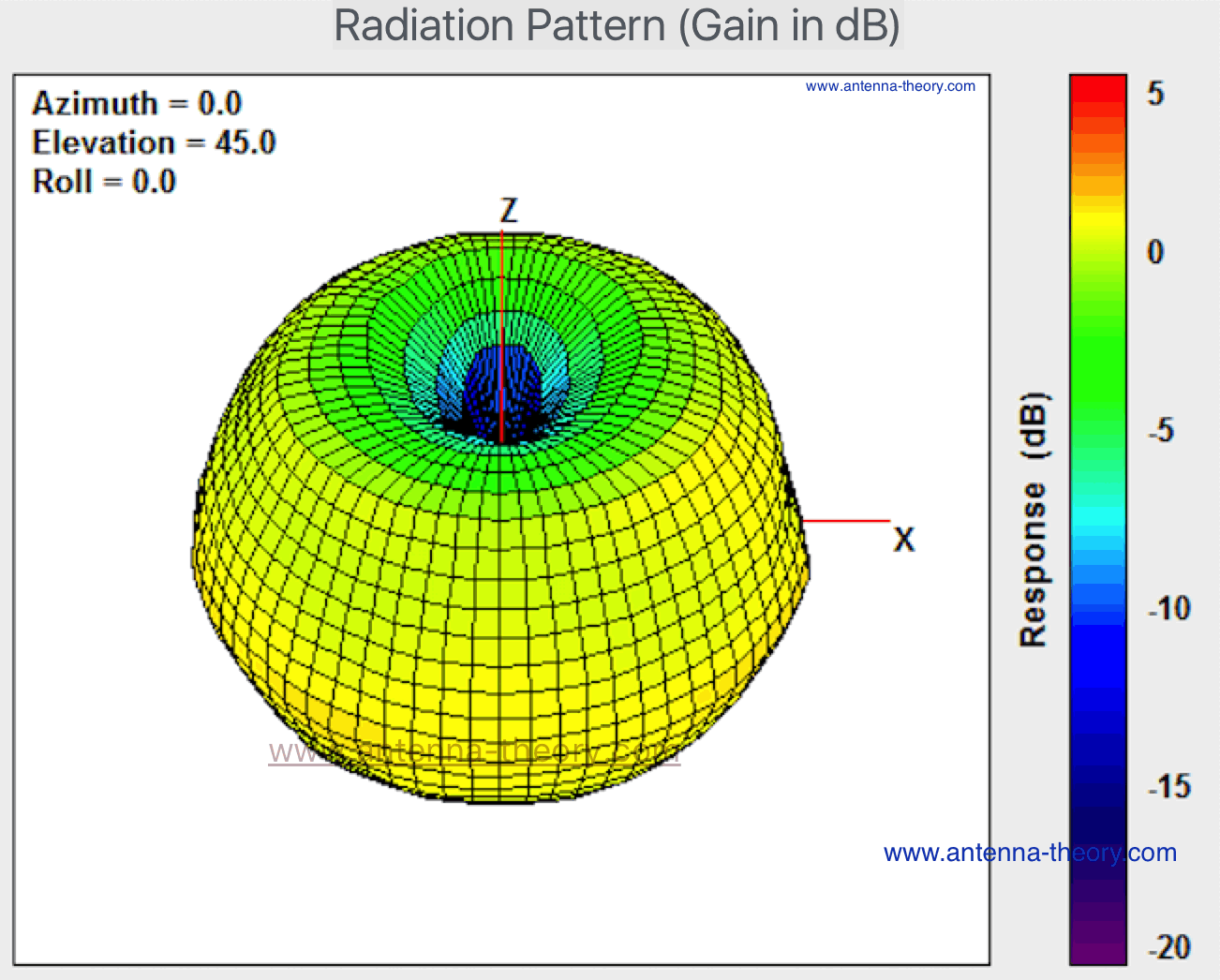
Satellite antenna gain formula. G t 30 10 log 350 30 25 4 4 6 dbk. Short dipole antenna but can never theoretically be less than 0 db however the peak gain of an antenna can be arbitrarily low because of losses or low efficiency. Antenna factor or correction factor is defined as the ratio of the incident electromagnetic field to the output voltage from the antenna and the output connector. The notions of efficiency and directivity depend on the following.
Directivity can be as low as 1 76 db for a real antenna example. Antenna gain calculator example. Gain dbi the ratio of the signal received or transmitted by a given antenna as compared to an isotropic or dipole antenna. The gain of a real antenna can be as high as 40 50 db for very large dish antennas although this is rare.
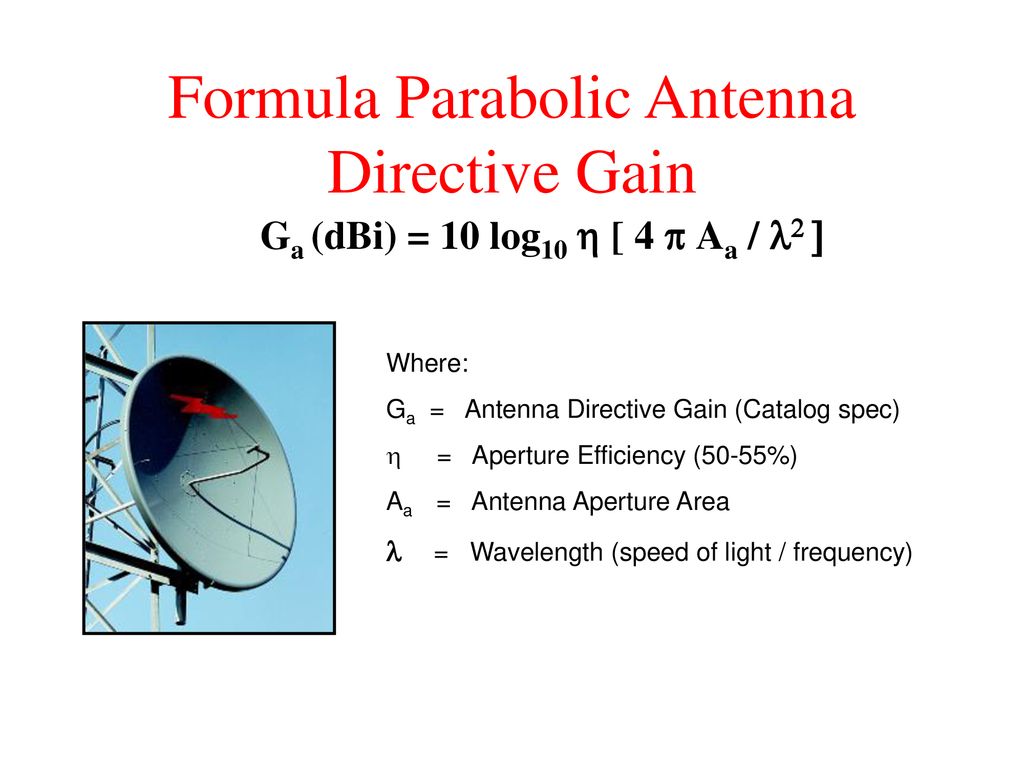
The standard definitions of terms for antennas ieee std 145 1993 defines free space loss as the loss between. It is very useful in rf system link budget calculation and analysis. Applying the above formula to the 25 meter diameter antennas often used in radio telescope arrays and satellite ground antennas at a. Antenna efficiency 0 7 antenna diameter 4 2 meter antenna frequency 6 ghz output gain dbi 47.
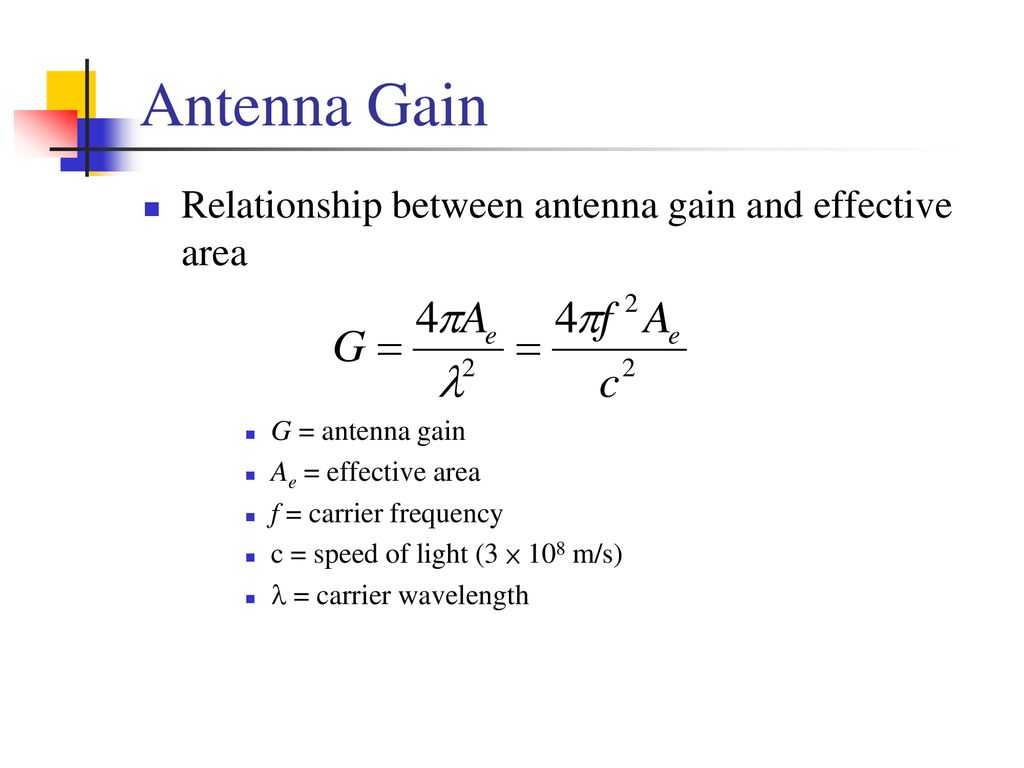
For antennas which are not defined by a physical area such as monopoles and dipoles consisting of thin rod conductors the aperture bears no obvious relation to the size or area of the antenna an alternate measure of antenna gain that has a greater relationship to the physical structure of such antennas is effective length l eff measured in metres which is defined for a receiving antenna as. A spacecraft whose beam is pointed substantially at cold space such as an inter satellite link or aimed at a distant planet etc would have a negligible noise contribution from the background. Antenna gain is the measure of amount of boost provided to the input sigal by the antenna. Antenna gain can only be achieved by making an antenna directional that is with better.
Friis original idea behind his transmission formula was to dispense with the usage of directivity or gain when describing antenna performance. In their place is the descriptor of antenna capture area as one of two important parts of the transmission formula that characterizes the behavior of a free space radio circuit. In the overall gain formula for the antenna an efficiency factor is included. Typically this may be between 50 and 70 dependent upon the actual antenna.
These are all multiplied together to give the overall efficiency. The efficiency of an antenna is the total radiated power divided by the input power at the feedpoint a transmitting antenna is supplied power by a feedline a transmission line connecting. G t antenna gain 10 log system noise temperature dbk. Power gain or simply gain is a unitless measure that combines an antenna s efficiency and directivity d.