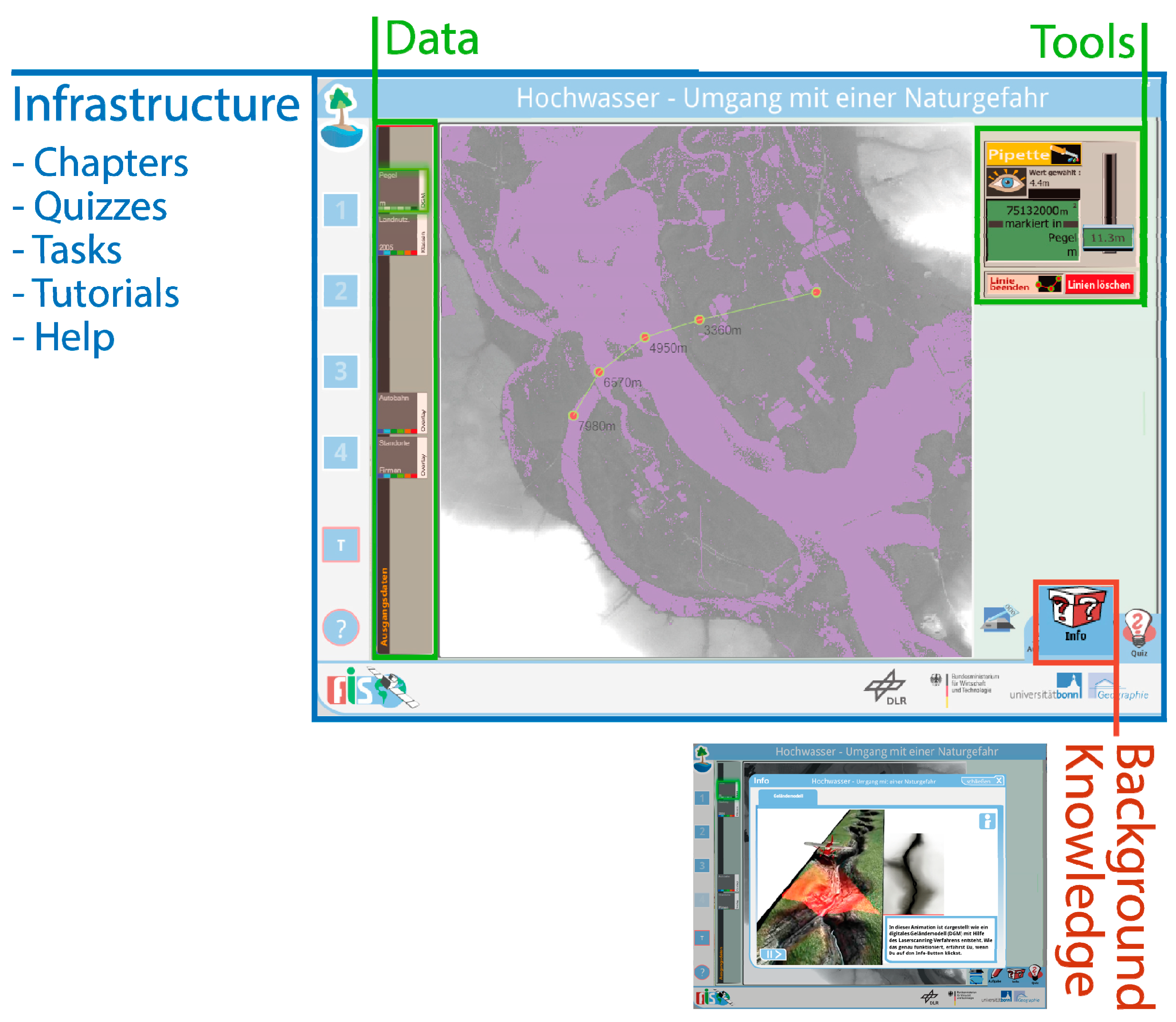
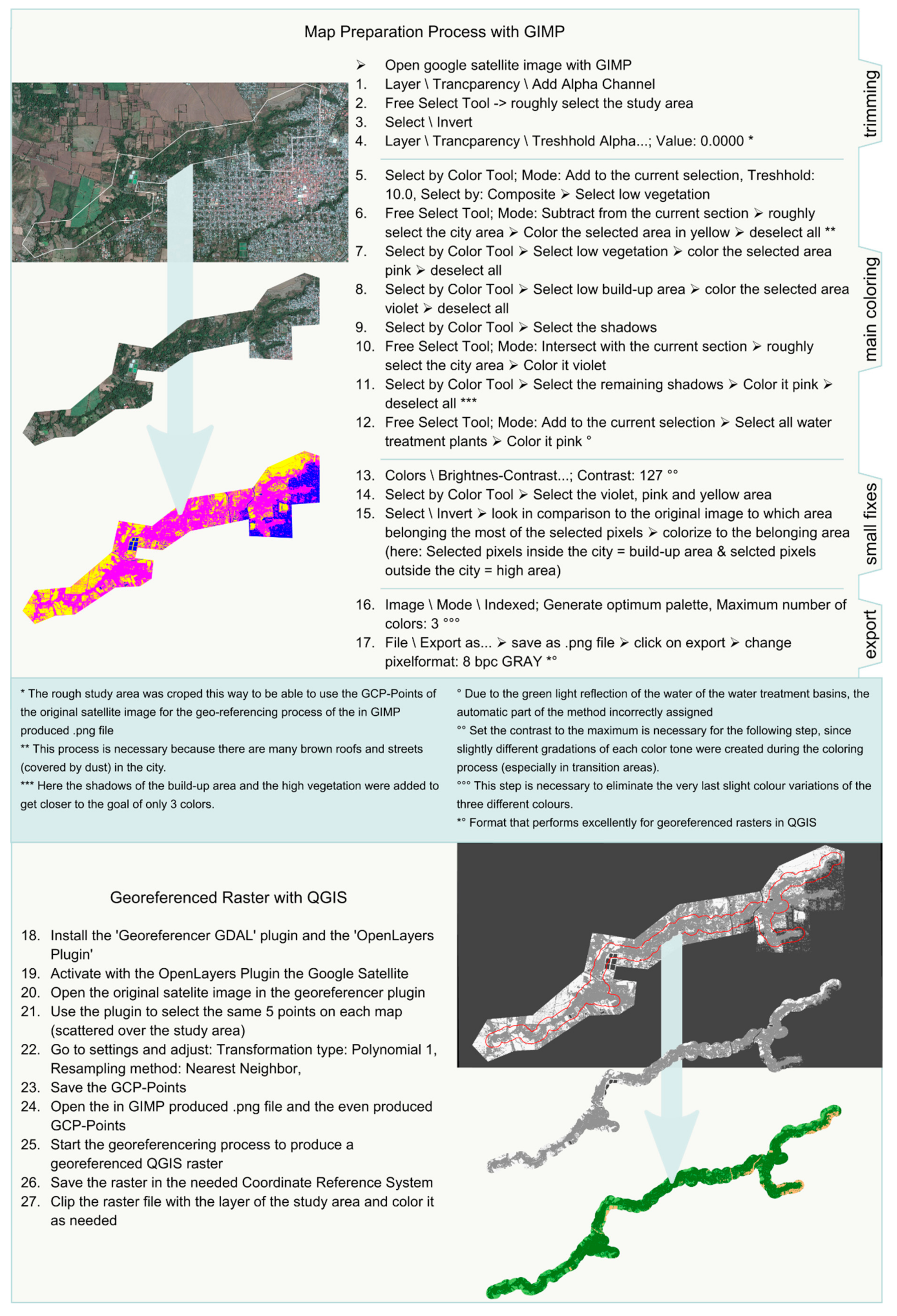
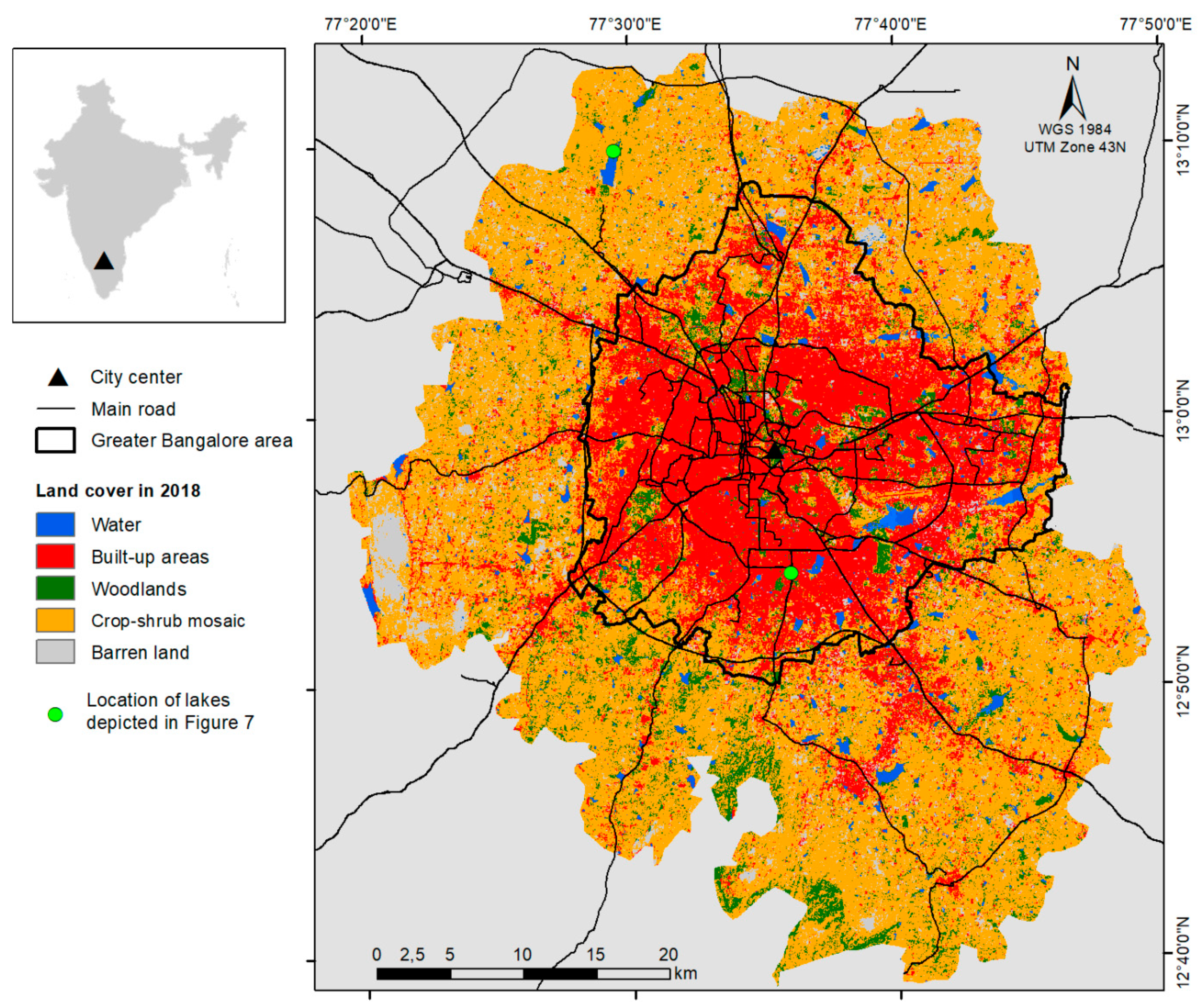
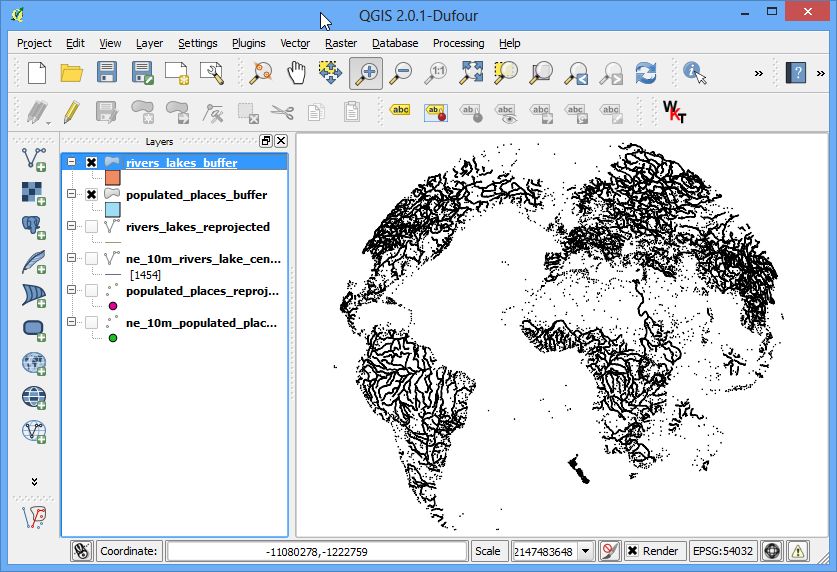
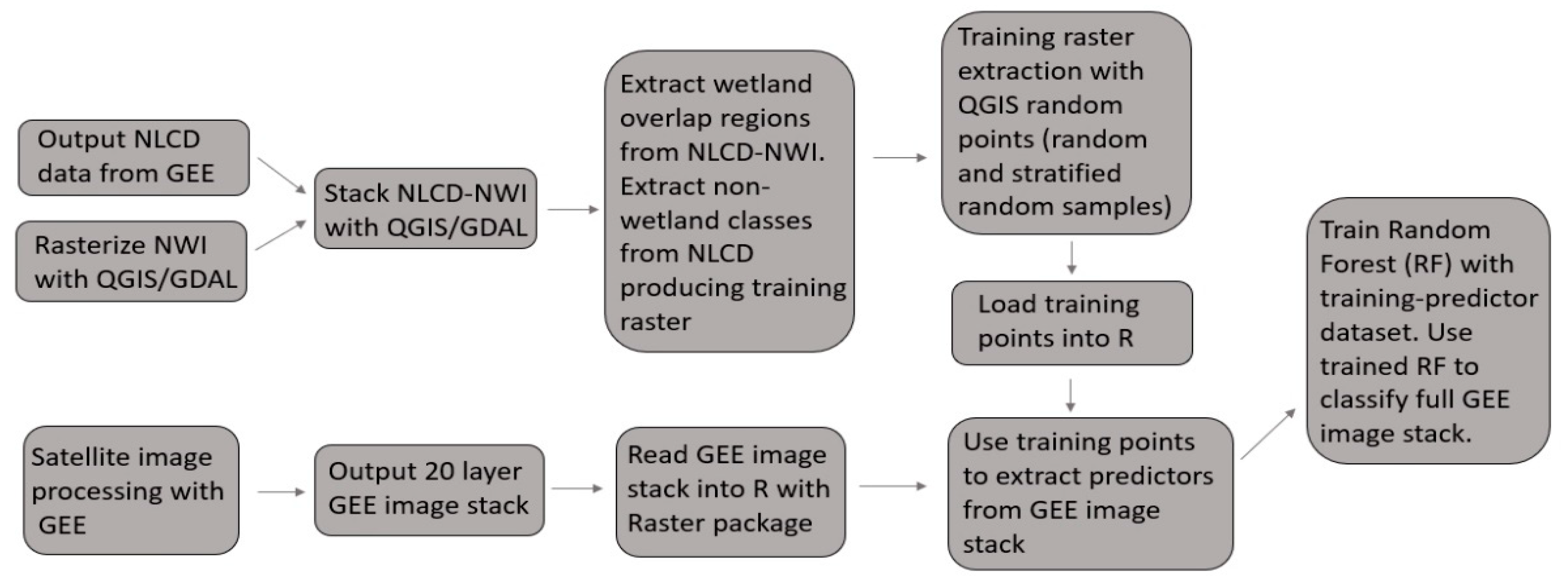
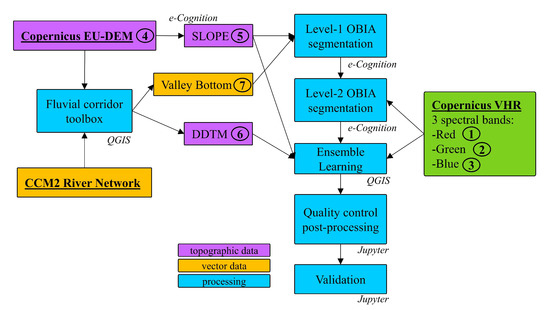
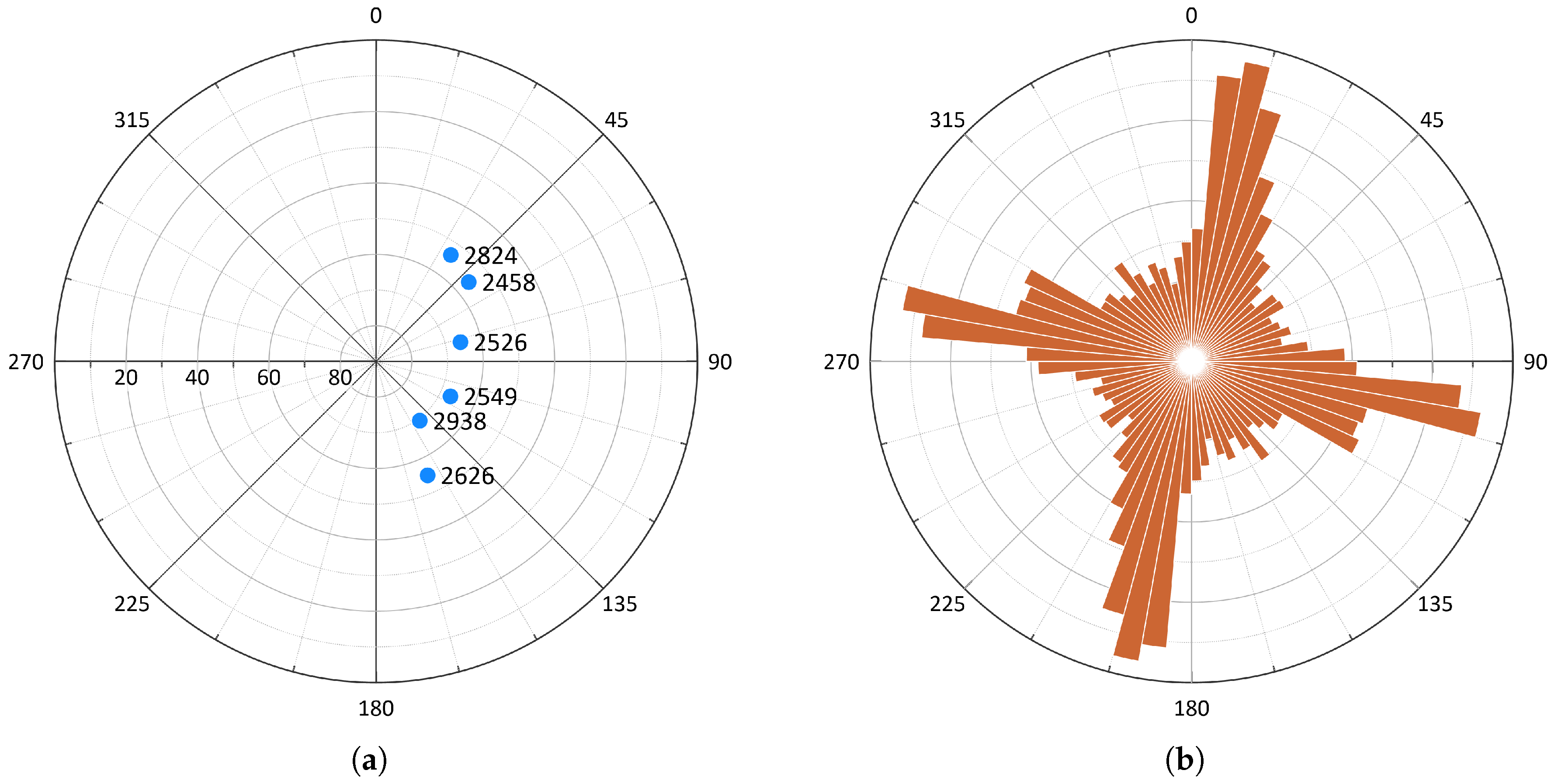
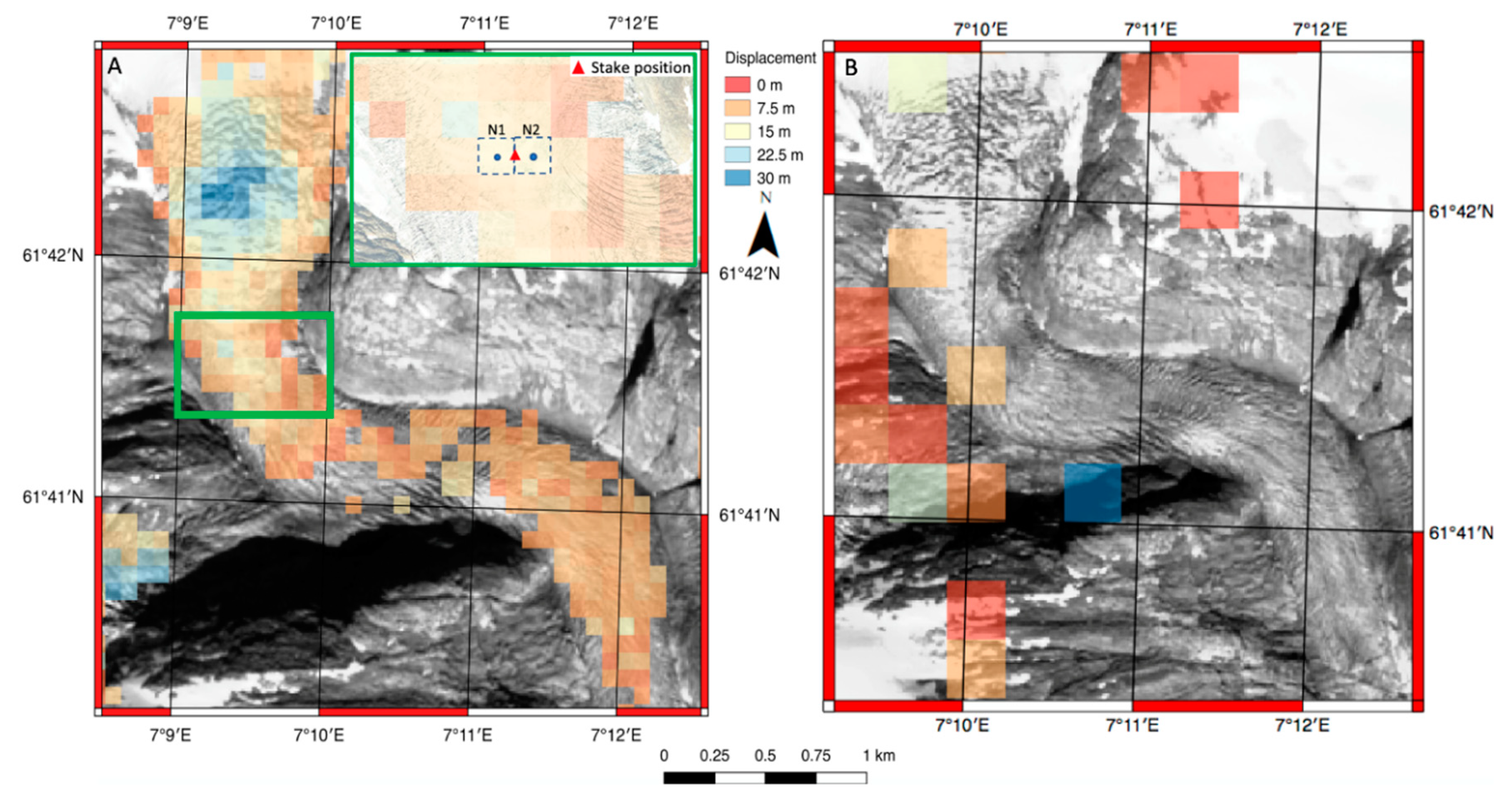
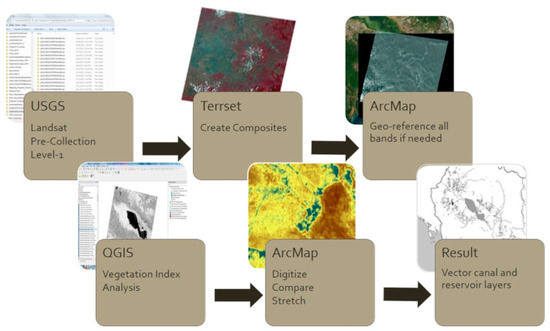
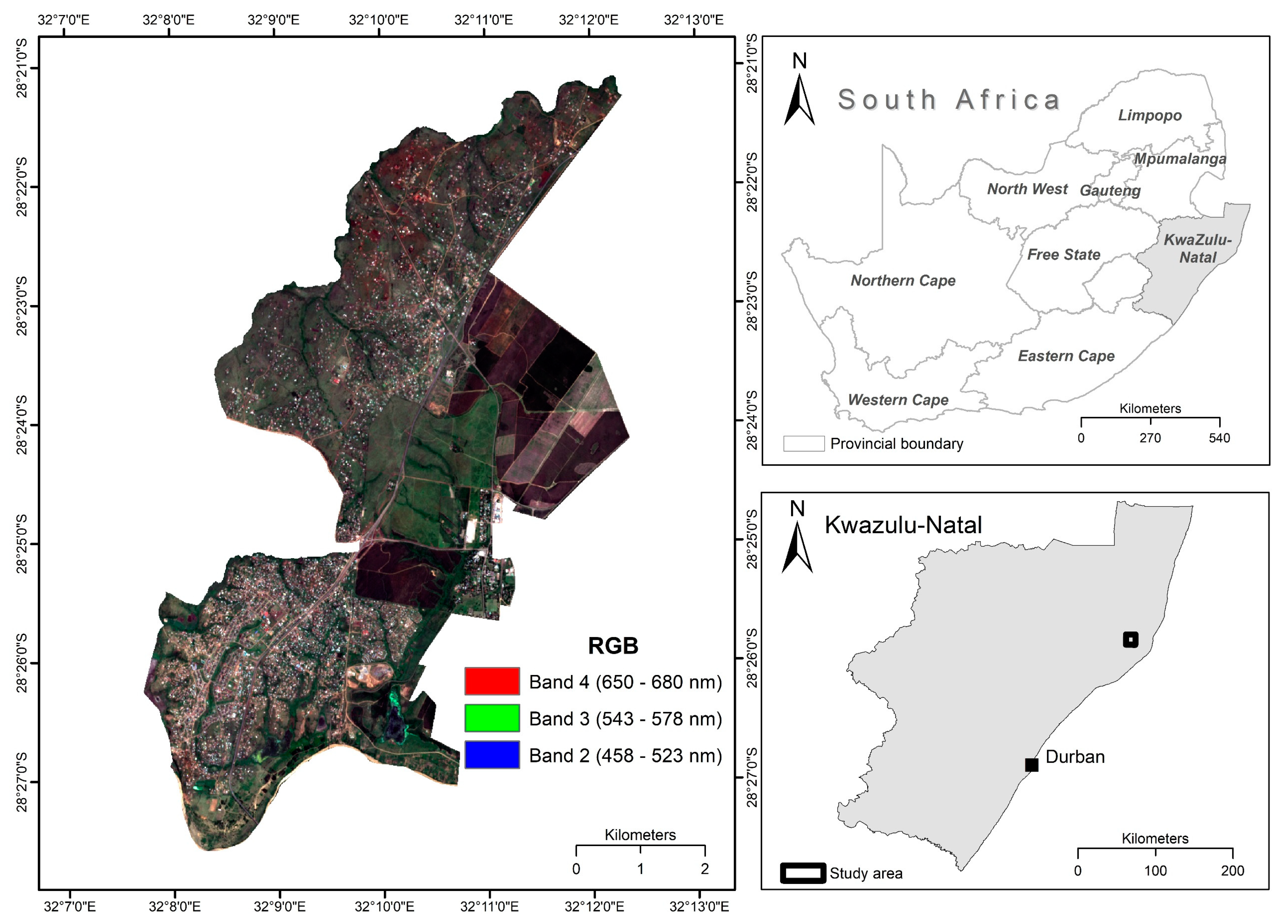
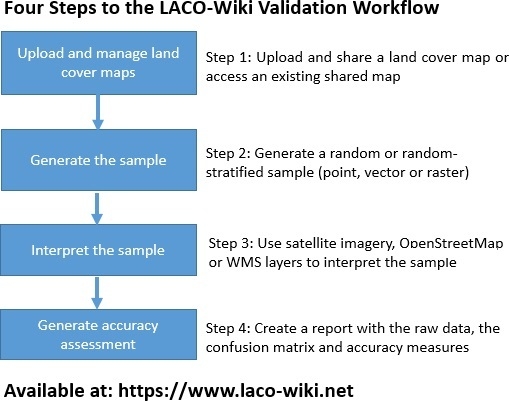
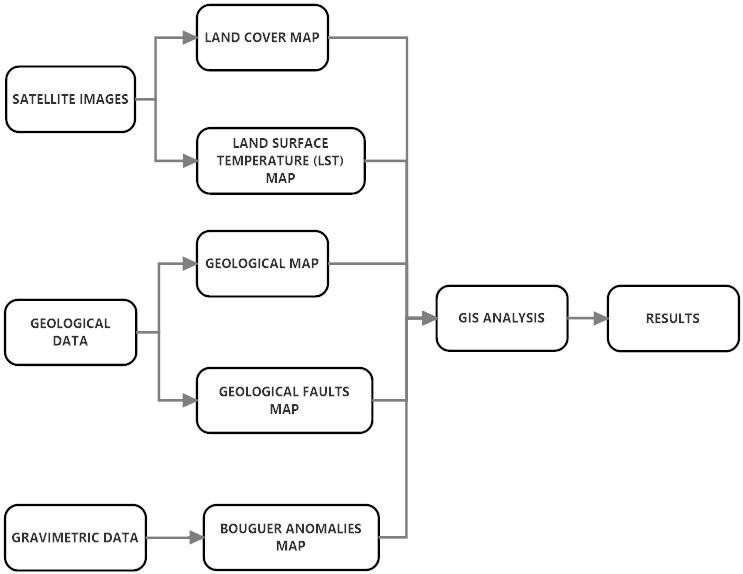
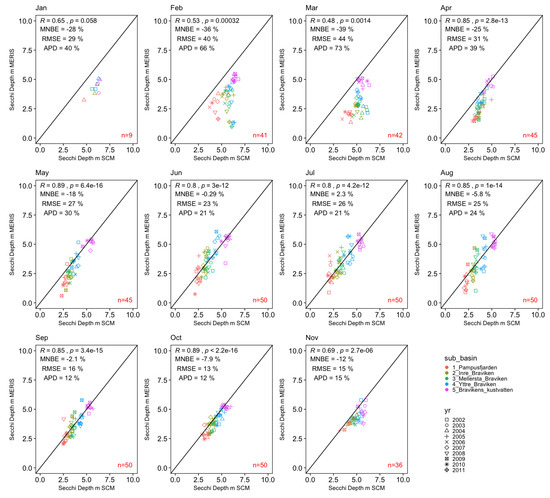
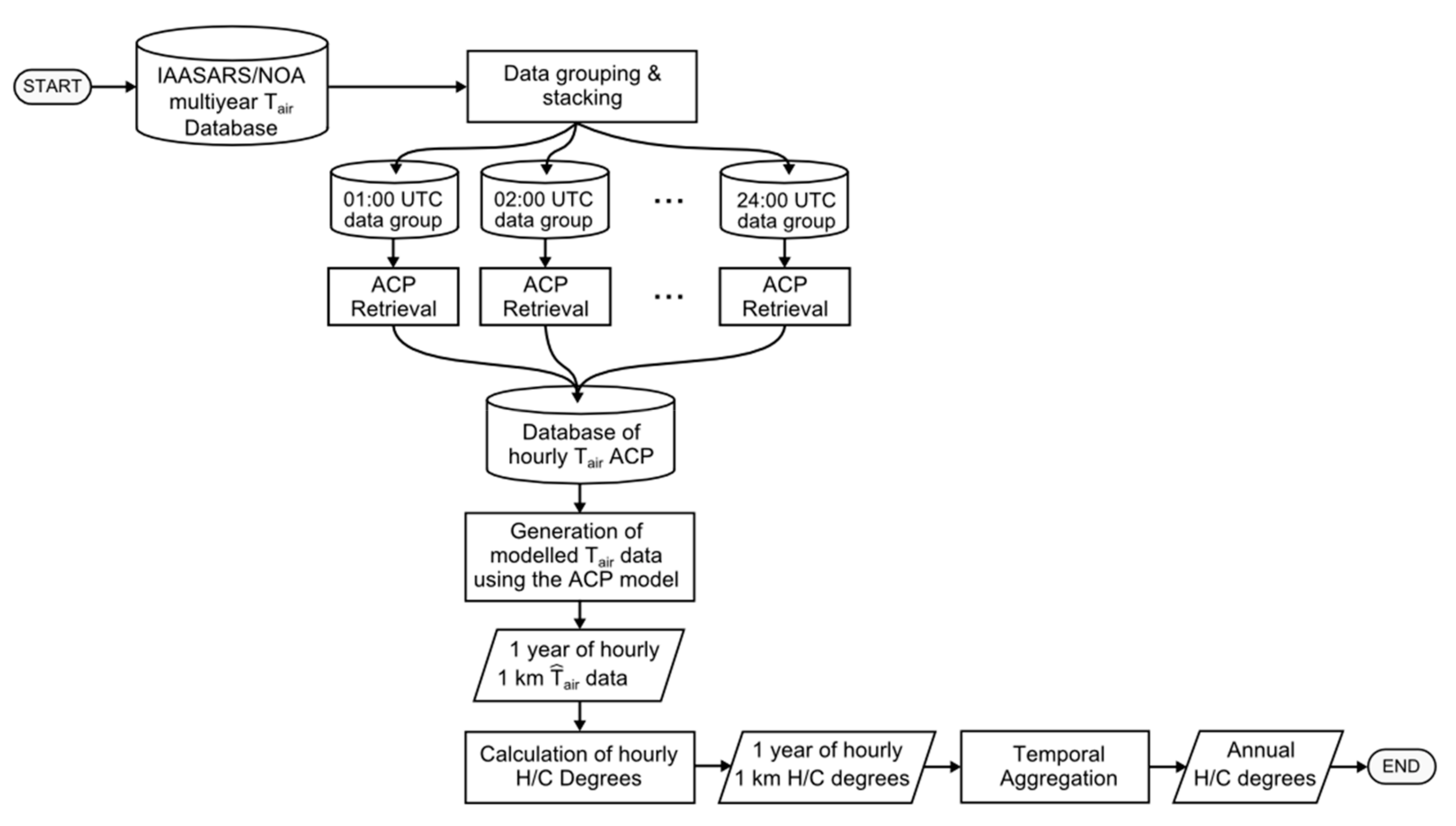
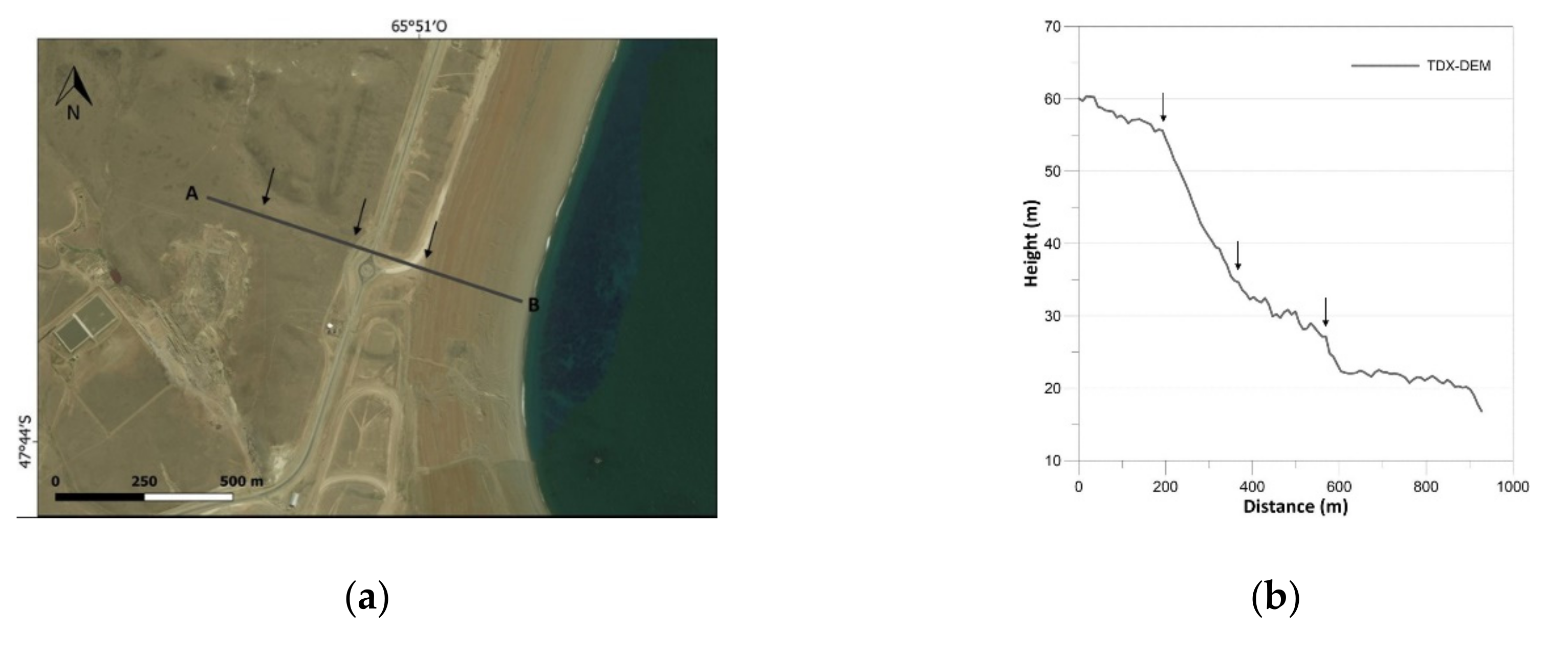
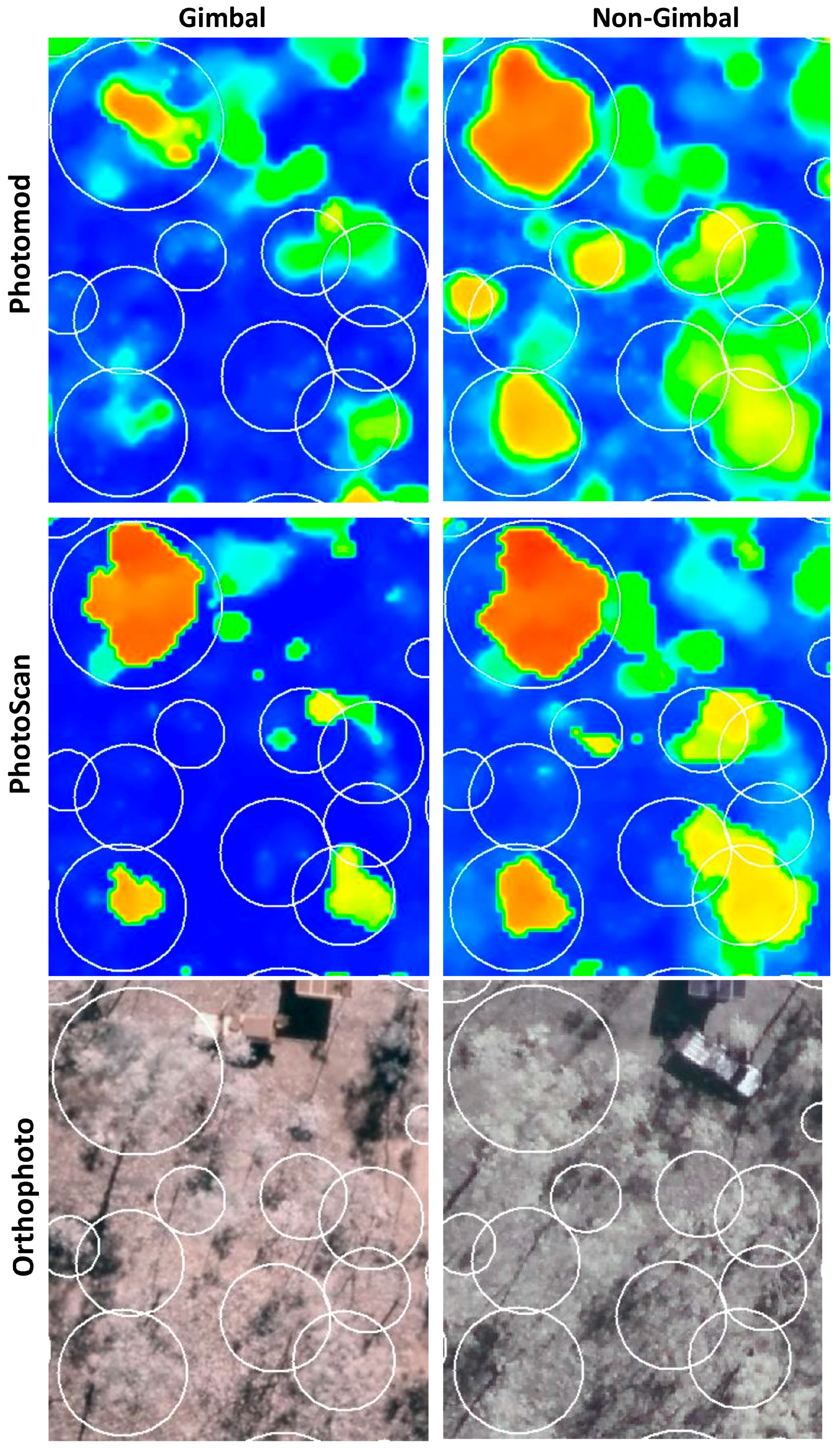
Satellite Derived Bathymetry Qgis
Satellite derived bathymetric sdb remote sensing research utilizes ocean optics to estimate near shore bathymetry elevation values using satellite imagery acquired from landsat 8 or digitalglobeworldview platforms.
Satellite derived bathymetry qgis. The maximum depth can be estimated by the module is depending up on many factors such as quality of the water suspended materials etc lyzenga et al 2006 kanno and tanaka 2012. The satellite derived bathymetry procedure was developed using a us calibration study site rockport massachusetts which has a low energy wave environment with a tidal range of about 2 5m. Researchers have investigated sdb algorithms over the last 30 years and proposed estimation methods. Description i image bathymetry is used to estimate satellite derived bathymetry sdb.
Module estimates bathymetry over near shore region using limited reference depth points. Coastal blue green and infrared bands are used to derive band ratio elevation profile estimates commonly known as the natural logs approach. Satellite derived bathymetry of mutton shoal with a color range scale that is correlated with the color scale used for multibeam processing. The pixel value of the satellite derived bathymetry image is obtained with the reference of hydrographic chart point value and so there is no need to measure the tidal height during the image acquisition.
It is important to note that only a few carefully selected chart soundings are used in the procedure to reference the satellite derived bathymetry to the. The depth range considered in the present work is up to 20 m. Since the images are based on attenuation of color bands depth can only be inferred so survey equipment such as vertical beam and multibeam sonars is necessary to acquire true depth. In contrast to other survey methods it requires no mobilisation of persons or equipment provides rapid access to bathymetric data and saves costs.